Why Transactions Fail: Common Error Messages and Their Solutions
Encountering error messages during crypto transactions leaves users, especially beginners, confused and unsure of how to proceed further. Although crypto offers faster transactions with fewer fees compared to traditional finance payments, transactions are more prone to failure. The major reasons for such crypto transactional failures include insufficient funds, network congestion, technical glitches, and more.
Aug 23, 2024
Encountering error messages during crypto transactions leaves users, especially beginners, confused and unsure of how to proceed further.
Although crypto offers faster transactions with fewer fees compared to traditional finance payments, transactions are more prone to failure. The major reasons for such crypto transactional failures include insufficient funds, network congestion, technical glitches, and more.
In this article, we'll explore the major reasons for crypto transaction failures, the error messages associated with such issues, and the best possible solutions to address them.
Why Crypto Transaction Failures Matter?
According to Cointelegraph research, 50% of the KYC-completed fiat-crypto transactions fail. Additionally, the authorization rate is even lower in Africa, at 8%, followed by South America (21%) and Asia (30%).
Enabling a smooth transactional experience for crypto users is essential to foster the industry. Frequent failures while sending, receiving, or staking digital assets will discourage both existing and new users from conducting crypto transactions.
Educating users to follow the best transactional practices, such as choosing high liquidity tokens, helps them significantly reduce failure rates.
Common Error Messages and Their Solutions
Rate Expired Error
It is common to receive a 'rate expired' error if it takes longer to confirm transactions on crypto platforms. Most platforms offer at least a 10-second window before refreshing with a new price and gas fees.
Once you encounter this error, no fees will be deducted from your wallet, but you can't proceed with your transaction at the rate that you previously agreed upon. You need to retry your transaction based on the updated rate.
For example, suppose you agreed to buy SOL tokens based on the market price of $150. The platform takes the possible volatility risk by locking the price so that you can complete the transaction at $150 for a specific time.
Solutions
Check the price refresh rate of the crypto platform before conducting the transaction to avoid rate expired errors. This is particularly important on centralized exchanges, as decentralized platforms typically don't have fixed refresh rates. However, regardless of the platform, ensure a stable internet connection before proceeding with any crypto transaction.
Payment Failed Error
Transactions that fail to finalize due to payment-related issues fall under the 'payment failed' error category.
For instance, in Stacks, this error might arise if a transaction involving the native STX token transfer is incomplete, meaning it’s either not processed at all or only partially processed.
Solutions
Ensure your Leather wallet has sufficient funds to cover the transaction, including the cryptocurrency you're sending and any associated network fees. These fees can vary depending on network congestion and the specific blockchain you're using.
It's advisable to have a small buffer to account for these fluctuations and prevent your transaction from failing due to insufficient funds.
Unconfirmed and Pending Transactions Error
An unconfirmed and pending transactions error occurs when your transaction has been initiated but hasn't been validated and added to the blockchain. This means it's waiting to be included in a block by miners or validators, depending on the specific blockchain mechanism.
For example, pending transactions on Bitcoin exist in a mempool that acts as a waiting area until the confirmation. Entering the wrong wallet address might also result in a pending transaction that will eventually become a failed transaction.
Network congestion is a major factor determining the speed at which transactions are updated on the respective blockchains, especially during peak trading hours. When congestion rates peak, it leads to a backlog of pending and unconfirmed transactions.
Solutions
You can use the Leather browser extension’s activities tab to increase the fee to complete the pending transaction in less time. Also, double-check the recipient’s wallet address, as the address of Bitcoin or Stacks differs from that of Ordinals, resulting in pending transactions.
Go through the Leather guidelines before initiating Ordinals, BRC-20 tokens, or Bitcoin transactions. For example, to send Ordinals, users need to enter the Taproot address starting with bc1p in the ‘Collectibles’ section and hit “send”.
One of the best options is to plan for your transactions during low network congestion, which can be analyzed with the help of free online tools. If the transaction is not urgent, it is better to wait until the process is completed.
Out of Gas Error
When you encounter an 'out of gas' error, it means that the fee for that particular crypto transaction is below the required threshold.
You can view such failed transactions on block explorers, such as Etherscan transaction status, as "fail" and "Out of gas" messages just below the receiver's wallet address section.
Solutions
Always ensure you have a clear understanding of the estimated gas fees required for your transaction. Leather wallet typically provides this estimate before you confirm a transaction.
It's advisable to have sufficient funds in your wallet to cover both the transaction amount and the gas fee. In some cases, increasing the gas limit you're willing to pay can help your transaction get processed faster, especially during periods of high network congestion.
Leather also suggests different fee amounts ranked in the order of percentile of fees for successful transactions. The “Standard” fee amount is selected by default, which corresponds to the 50th percentile.
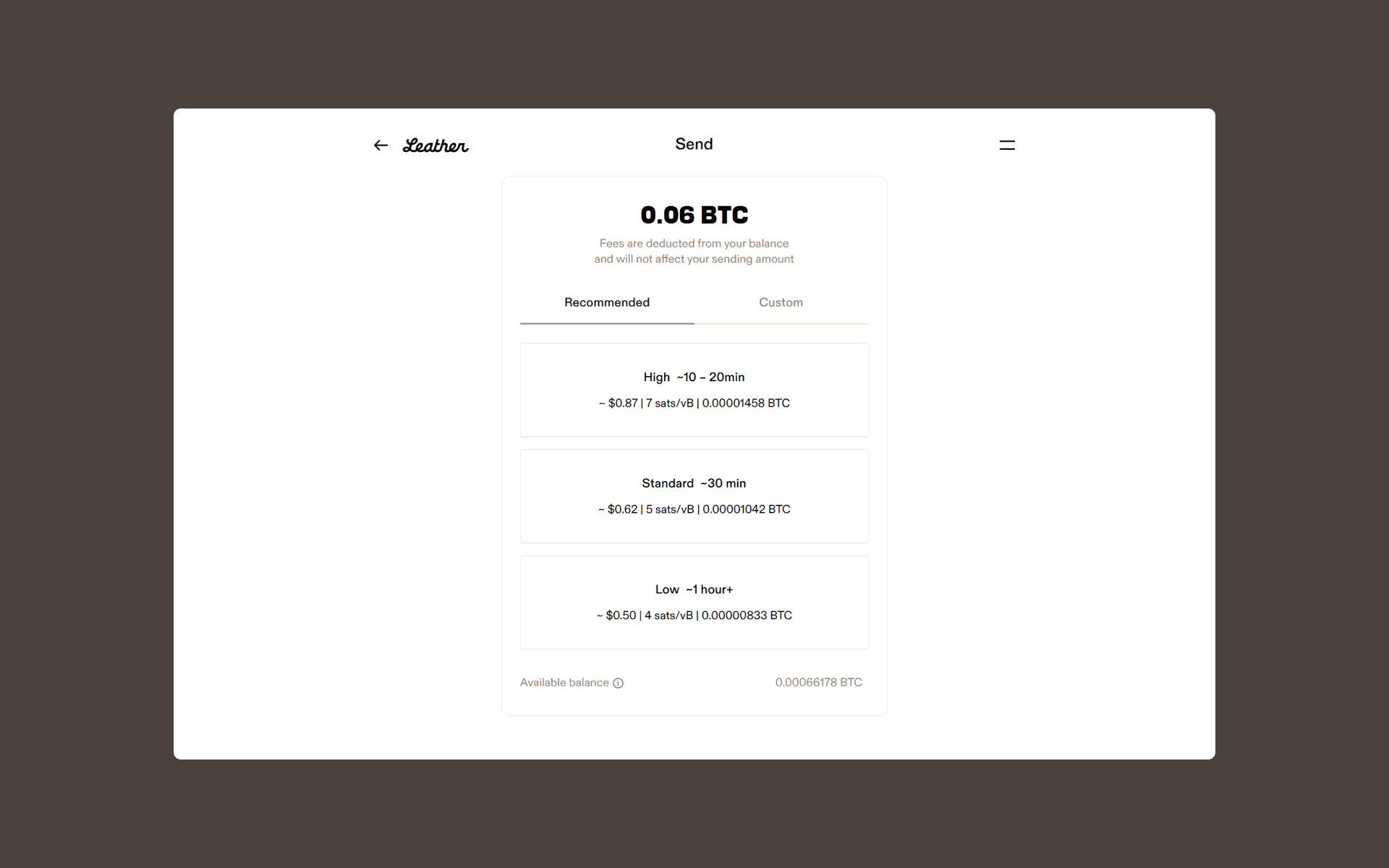
Dust UTXO Error
Dust refers to the tiny amount of tokens, which is a kind of unspendable present in Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) model-based cryptos such as BTC, LTC, BCH, DOGE, etc.
Your transaction for these cryptos shows a UTXO error as the token's value is less than the fees charged.
For example, let's suppose that a wallet address contains a balance of 0.0065 BTC and four UTXOs of 0.0048, 0.0009, 0.0006, and 0.0002. As this BTC wallet has three dust UTXOs (0.0009, 0.0006, and 0.0002), it results in a 'dust UTXO error' when attempting to transact the overall available 0.0065 BTC.
Solution
One of the best methods that you can follow to avoid 'dust UTXO error' is to refrain from sending tokens that are valued below the transaction fees.
Leather addresses the dust UTXO error by ensuring that each transaction leaves a sufficient amount of satoshis (at least 546 sats) with the inscription to stay above the dust limit. The process involves calculating the difference between the total output and the sat offset, ensuring the fee leaves enough sats to avoid the dust error. This precise calculation helps in unravelling inscriptions while avoiding dust UTXO issues.
Conclusion
The transactional failures discussed in this article are the most common ones in the crypto space. Selecting platforms with high liquidity, opting for a higher gas fee, maintaining enough token balance, and choosing a low congestion period can help you avoid common errors such as 'unconfirmed' and 'pending' transaction errors.
Choosing the right wallet, such as Leather, can also significantly reduce transaction errors by leveraging built-in features designed to handle these issues. Leather provides precise calculations to avoid dust UTXO errors, automatic fee adjustments to avoid out-of-gas errors, and guides to ensure correct transaction procedures. These integrated solutions help users navigate the complexities of crypto transactions more smoothly, reducing the likelihood of encountering common errors.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Always conduct your own research before engaging in crypto transactions.