Help Center
Multi-Signature Wallets: Definition and Use Cases
Jun 12, 2025
Leather does not have control over the security measures of external wallets or the actions of users. Users are responsible for managing their own digital signatures and transaction approvals.
A multi-signature (multi-sig) wallet is a cryptocurrency wallet in which two or more people vouch for all ongoing transactions. While multi-sig wallets need a more technical setup, they provide added security for crypto assets. Ultimately, multi-sig wallets reduce the chances of digital assets being stolen with just a password or wallet key.
What Are Multi-Signature Wallets?
A regular single-signature wallet normally only requires one key that belongs to a single Bitcoin user to gain access to it and the funds inside. A multi-sig wallet, on the other hand, allows more than one digital signature to move bitcoin. The addresses assigned to a multi-sig wallet determine how many digital signatures are needed to approve a transaction. For example, two online users can have a multi-sig wallet allowing each of them to sign off on a transaction. However, the wallet does not necessarily require both users’ signatures unless they set up the wallet to need both keys.
The main issue with single-sig wallets is that because they only require one key, the wallet could be hacked into or stolen if it were to be compromised. Multi-sig wallets resolve this issue by requiring a certain number of keys, though how many are needed depends on how many signers are attached. However, unless it’s a 1-of-2 multi-sig wallet, a hacker cannot breach a wallet with just one key as they'll need multiple to do so.
Additionally, since multi-sig wallets are built on smart contracts, signers can use them to establish the rules for accessing funds and approving transactions. If the signers have any specific security preferences or requirements, they can customize their multi-sig wallets as they see fit.
How Does a Multisig Wallet Work?
While anyone can start a transaction, it won't be finalized until a certain number of signers approve it. Until then, the transaction will remain "pending." A multi-sig wallet carries out this procedure by implementing one of two settings: N-of-M or N-of-N.
N-of-M
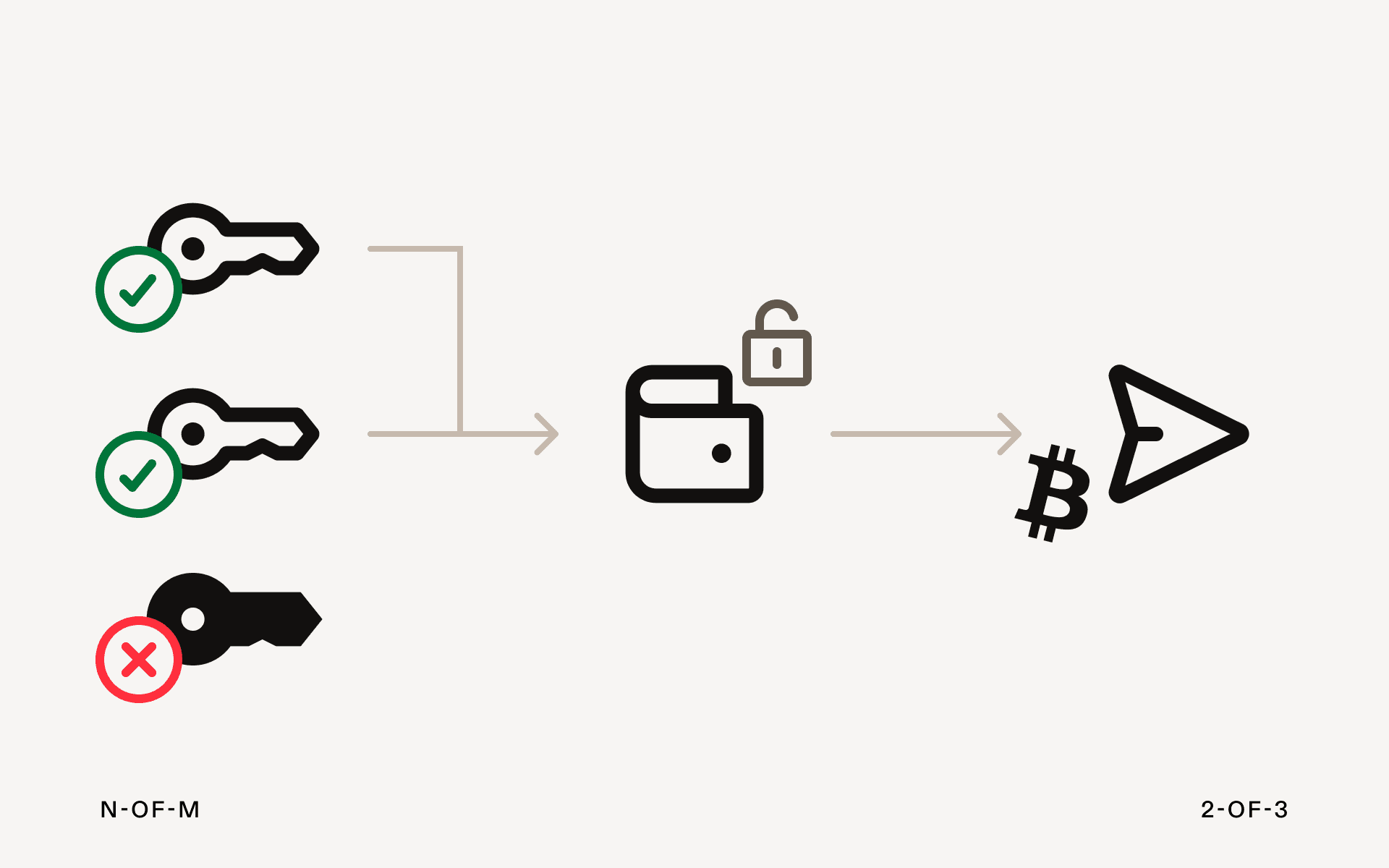
Only a certain subset of signers (N) out of the total number of signers (M) are needed to approve a transaction. While the exact configurations depend on the total number of signers in any particular multi-sig wallet, some examples include:
- **1-of-2: **Only one user can approve transactions and does not need the approval of the other one.
- **2-of-3: **At least two signers need to approve any initiated transaction.
- **3-of-5: **Three out of five parties must sign off on a transaction.
N-of-N
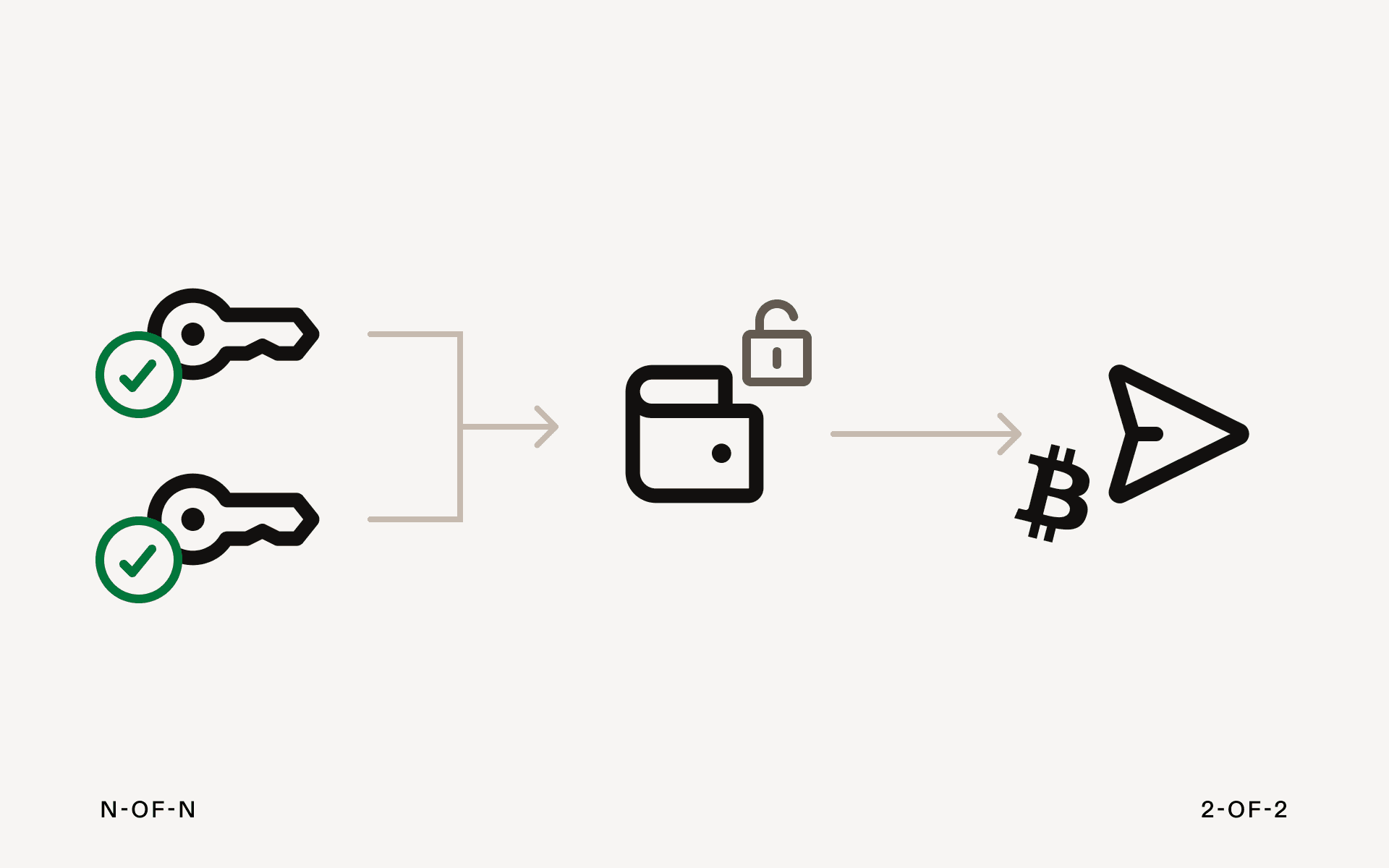
All N-designated signers must unanimously agree on whether a transaction takes place. Like N-of-M, the configurations depend on how many users are involved and what the transaction entails. For example:
- 2-of-2: Also known as the “duo signature” wallet, both designated signers must agree on a transaction before it can be validated. While either party can initiate a transaction, the funds remain in the wallet until both users approve the transaction.
Potential Risks and Disadvantages of Multi-Sig Wallets
Unfortunately, multi-sig wallets have risks and disadvantages despite their various security features and benefits. Some of these include:
- Centralization risks: To maximize security, the keys of all parties involved in a multi-sig wallet must be distributed amongst the various signers. A single signer should never hold most of the keys since the multi-sig wallet will become vulnerable to hacking or theft if the keys are compromised. Similarly, hackers can access a 1-of-2 multi-sig wallet if they secure one of the two keys.
- Lack of flexibility: In exchange for an extra layer of security, multi-sig wallets are much less flexible and convenient than their single-signature counterparts. For example, multiple users need to coordinate with each other to not only set up a multi-sig wallet but also approve any initiated transactions. Parties become dependent on each other to authorize transactions, so if a certain amount becomes uncooperative or unavailable, the process becomes much slower.
Common Use Cases for Multisig Wallets
The most common use cases of Bitcoin users having multi-sig wallets typically come down to the fact that a group of them want to own and manage a single account. For example:
-
Shared business Accounts: To manage transactions and funds, some businesses configure their multi-sig wallets by requiring a certain number of executives to authorize a transaction. This allows these executives to control what transactions are made, thereby reducing the risk of theft and hacking.
-
Escrow payments and services: Escrow transactions and services typically utilize 2-of-3 multi-sig wallets in which a third party holds a key and is an arbitrator. If there's ever a dispute between the two signers, the arbitrator will hold all the funds and block both of them from accessing them until the issue has been resolved.
-
Joint accounts/ownership: Using a multi-sig wallet, friends and family members managed their shared finances and expenses under one account with each person given a certain amount of control. Platforms and protocols prioritizing security, decentralized control, and transparency are other notable examples that greatly benefit from using multi-sig wallets. These include:
-
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and other DeFI applications use multi-sig wallets to manage funds.
-
**Smart contract platforms: **Smart contract platforms like Ethereum use multi-sig wallets to integrate into smart contracts and ensure secure and transparent interactions.
-
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Multisig wallets give DAOs the ability to allow multiple parties to make decisions and control funds collectively.
Multisig Wallet Security
Unlike a single-signature wallet which typically only requires one private key, multi-sig wallets allow multiple keys (unless it’s a 1-of-2 multi-sig wallet) to sign off on transactions and give signers access to funds. By allowing more than one digital signature to move bitcoin, multi-sig wallets create an extra layer of security that regular single-signature wallets cannot provide.
Are Multi-Wallets More Secure?
Multi-sig wallets are generally considered more secure than regular, single-signature ones because multi-sig wallets allow more than one key to approve transactions. This is important because allowing multiple digital signatures rather than just one increases users’ ability to protect their wallets and funds from being compromised and stolen.
For example, because single-signature wallets typically only require one key to gain access to their funds, if the key were to get lost, stolen, or compromised by a hacker or malware infection, then it would immediately put the wallets at risk. That single key is the only tool that can access the wallet, so the user could risk losing access to their funds permanently if anything were to happen to it.
By comparison, multi-sig wallets provide more of a safety net because they allow more than one private key to authorize transactions and access funds. For example, if a key for a 2-of-3 multi-sig wallet were to be compromised or stolen, its assets would still be secure as the hacker would need at least 2 keys to break into the wallet.
Additionally, multi-sig wallets provide a wide range of security features that reduce the risks of fraud or theft from hackers who could negatively affect the assets inside. One of these features is a system called two-factor authentication (2FA). Under 2FA, all pending transactions must be validated by a certain number of users before they can be approved. This keeps signers in check as it stops malicious actors from accessing assets without authorization and revoking their access once caught.
The 2FA also ensures that the keys needed to access a wallet are kept at different locations or with different people. This reduces the chances of a bad actor getting their hands on all the keys. The users of a multi-sig wallet are the keepers of their keys.
Multi-Signature Wallets vs. Other Crypto Wallets
The most common type of wallet is the single-sig wallet which typically only requires one private key for a user to gain access to a wallet and approve transactions. While these single-signature crypto wallets provide a level of convenience that makes setting them up and authorizing transactions easy for Bitcoin users, they often come at the cost of high security. The user may permanently lose access to their wallet and its funds if the key gets stolen or compromised.
Some examples of wallets that are typically single-sig, though they have some features that give users the ability to configure them to multi-sig ones, are:
- Software wallets: These wallets are installed on a user’s electronic device (computer, laptop, mobile device, etc.) and then generate a private key (or keys) that are stored within the device on a server.
- Hardware wallets: These types of wallets produce and store keys in an offline, physical device. Multi-sig wallets allow multiple keys and digital signatures in which a certain number of signers are needed to sign off on transactions and manage funds. While these types of wallets are not as convenient or flexible as their single-sig counterparts as they require coordination from multiple people to set up and approve transactions, multi-sig wallets provide an extra layer of security to compensate. Depending on the type of wallet that's desired, multiple parties can determine how many keys are needed to approve transactions.
However, the ability to allow multiple signatures to approve a transaction is not unique to multi-sig wallets as Multi-Party Computation (MPC) wallets are another type that provides a similar benefit. MPC wallets break apart a private key into multiple shares that are held by various signers. Any transaction cannot be made nor can the wallet’s fund be accessed until the signers agree to combine their shares into a whole key.
Conclusion
While Leather is not a multi-sig wallet, it does connect you with multi-signature solutions like Asigna and emphasizes secure key storage. Not only is Leather incredibly accessible, as it is free to download and easy to install, but it is also self-custodial, giving users the ability to password-protect private keys from any potential hackers.