Help Center
Bitcoin NFTs: How Do They Work?
The post discusses Bitcoin NFTs and Ordinals, explaining their creation, use cases, and how to mint, buy, sell, and trade them using Leather. It also compares Bitcoin NFTs and Ordinals, discusses their investment potential, and reasons for their rising popularity.
Jun 18, 2025
Bitcoin NFT Use Cases
There are many use cases for Bitcoin NFTs, but these are the most common:
- Digital art and music tokenization
- Decentralized identity solutions
- Tokenization and ownership of real-world assets
- Digital collectibles
- Gaming assets
- Virtual real-estate ownership
- Cross-chain asset interoperability
- Access to decentralized finance (DeFi) applications
- Governance on Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
- Membership access to projects
- Event ticketing
How to Buy, Sell, and Trade Bitcoin NFTs with Leather
To buy, sell, and trade Bitcoin NFTs with Leather, follow these simple steps:
- If you don't have a Leather wallet set up, go to Leather’s website and download the Leather browser extension.
- Once installed, select "Create New Wallet" and follow the on-screen instructions. Make sure to back up your private keys securely to prevent loss of access. You can learn more about securing your Bitcoin wallet and opening a Bitcoin account here.
- After your wallet is created, fund it with some BTC or STX.
- Once funded, connect it to trusted Bitcoin NFT marketplaces like Gamma or Magic Eden.
- You will now be able to search available collections to buy and trade, as well as create and sell your own Bitcoin NFTs.
Bitcoin NFTs vs. Ordinals
While the term "Bitcoin NFT" is often used to refer to Ordinal inscriptions, it's important to know that the two are inherently different.
Bitcoin NFTs:
- Represent ownership of a specific digital item or piece of content.
- Can be traded, bought, and sold like traditional collectibles.
- Are minted by adding data about an asset to a smart contract on the Stacks blockchain.
- Store their data off-chain. Only a reference point is stored on-chain.
- Enable programmable features like royalties, interactive functionalities, and other complex interactions.
- Can only be non-fungible.
- Allow for larger files when minting.
Ordinals, on the other hand:
- Represent ownership of digital artifacts on the Bitcoin blockchain.
- Can be traded, bought, and sold like traditional collectibles.
- Are minted by inscribing (attaching) data about an asset to satoshis on the Bitcoin blockchain.All data is stored (inscribed) on-chain.
- Can be fungible or non-fungible.
- Have a file size limit of 4 MB per inscription, though developments like recursive inscriptions have addressed a number of challenges related to data size and Ordinals.
Are Bitcoin NFTs a Good Investment?
Only you can determine if Bitcoin NFTs are a good investment. Considering these factors will help you make conscious decisions:
- Bitcoin NFTs are expanding, allowing for considerable ecosystem growth and long-term potential.
- Bitcoin NFTs are secured by Bitcoin’s Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which has demonstrated exceptional resilience in comparison to other blockchains.
- Ordinals are stored directly on-chain, which makes them scarce and unique digital assets.
- On the flip side, price fluctuations can be common with Bitcoin NFTs.
- Ultimately, you need to think of why you want to own a particular Bitcoin NFT and assess if it would make a good investment based on that.
Why Are Bitcoin NFTs Rising in Popularity?
There are several reasons why Bitcoin NFTs are rising in popularity:
- The entire Bitcoin ecosystem is growing rapidly, which affects the growth of Bitcoin NFTs.
- They are fairly new to the ecosystem, and that brings attention from experienced and new users.
- They represent a novel way to create unique digital assets, offering new use cases.
- With Ordinals, users can store data directly onto the blockchain, which many consider beneficial.
- They are associated with Bitcoin’s brand and cryptocurrency, which is the most used and well-known of the entire crypto ecosystem.
- Many Bitcoin NFTs are tied to meme culture, which is very popular in the crypto space.
- After the Ethereum NFT boom, collectors and investors see Bitcoin NFTs as a good opportunity to diversify investments and explore other digital assets. Bitcoin NFTs and Ordinals bring unique digital ownership possibilities to the Bitcoin ecosystem, allowing users to create, own, and trade digital assets. They can be minted on a layer 2 like Stacks or inscribed directly onto satoshis in the Bitcoin base layer.
Bitcoin NFTs offer an array of use cases that span from digital art to tokenization of real-world assets, and while not everyone holds Bitcoin NFTs for investment purposes, many do consider them for this purpose.
What are Bitcoin NFTs?
Bitcoin NFTs are non-fungible tokens created in the Bitcoin ecosystem. They work differently depending on whether they are minted on the Stacks blockchain or inscribed through the Ordinals protocol.
On the Stacks blockchain, Bitcoin NFTs are minted using smart contracts. The data is stored off-chain but secured by Bitcoin’s base layer. Only a reference point is stored on-chain.
This gives Bitcoin NFTs many benefits, such as programmable features and larger file sizes.
The Ordinals protocol allows data to be directly inscribed onto satoshis. This means that Ordinals live completely and permanently on the Bitcoin base layer, making these Bitcoin NFTs more secure and scarce but can limit their capabilities for programmable features and file sizes.
Where Did Bitcoin NFTs Come From?

The genesis Bitcoin block is considered the foundation of what we know today as Bitcoin NFTs.
It included a message referencing a news headline showing the capability for adding information to Bitcoin transactions. This capability led to the creation of Namecoin, which demonstrated that the Bitcoin blockchain could be used to store and transfer data beyond financial transactions.
In 2013, Colored Coins were born as a first step in introducing non-fungibility to Bitcoin. These coins could be used to represent real-world or digital assets.
Counterparty—a protocol built on top of Bitcoin—was born one year later. It facilitated the creation of NFTs on the Bitcoin blockchain, and projects like Rare Pepes and Spells of Genesis introduced the concepts of NFT collections and trading card ownership.
The launch of the Stacks protocol in 2021 offered a new and scalable approach to Bitcoin NFTs. This Bitcoin Layer 2 allowed for NFTs to be created off-chain but settled on the main chain, making transactions faster and saving space in the blocks.
In 2023, Ordinals swept onto the scene to offer digital artifacts inscribed completely on-chain, offering new possibilities but bringing back concerns about block congestion and usage.
How Do Bitcoin NFTs Work?
There are two different ways in which the community has made Bitcoin NFTs work on Bitcoin:
- They can be minted on a Layer 2 blockchain like Stacks.
- They can be inscribed directly onto the Bitcoin blockchain thanks to the Ordinals protocol.
How Do Bitcoin NFTs Work in the Stacks Ecosystem?
In the Stacks ecosystem, Bitcoin NFTs work thanks to smart contracts. They can be minted on the Stacks layer while being secured by the Bitcoin base layer.
When a Bitcoin NFT is minted in the Stacks layer, the data—images, videos, audio, or text—is stored off-chain. What is minted and stored on Stacks is a reference point to that data.
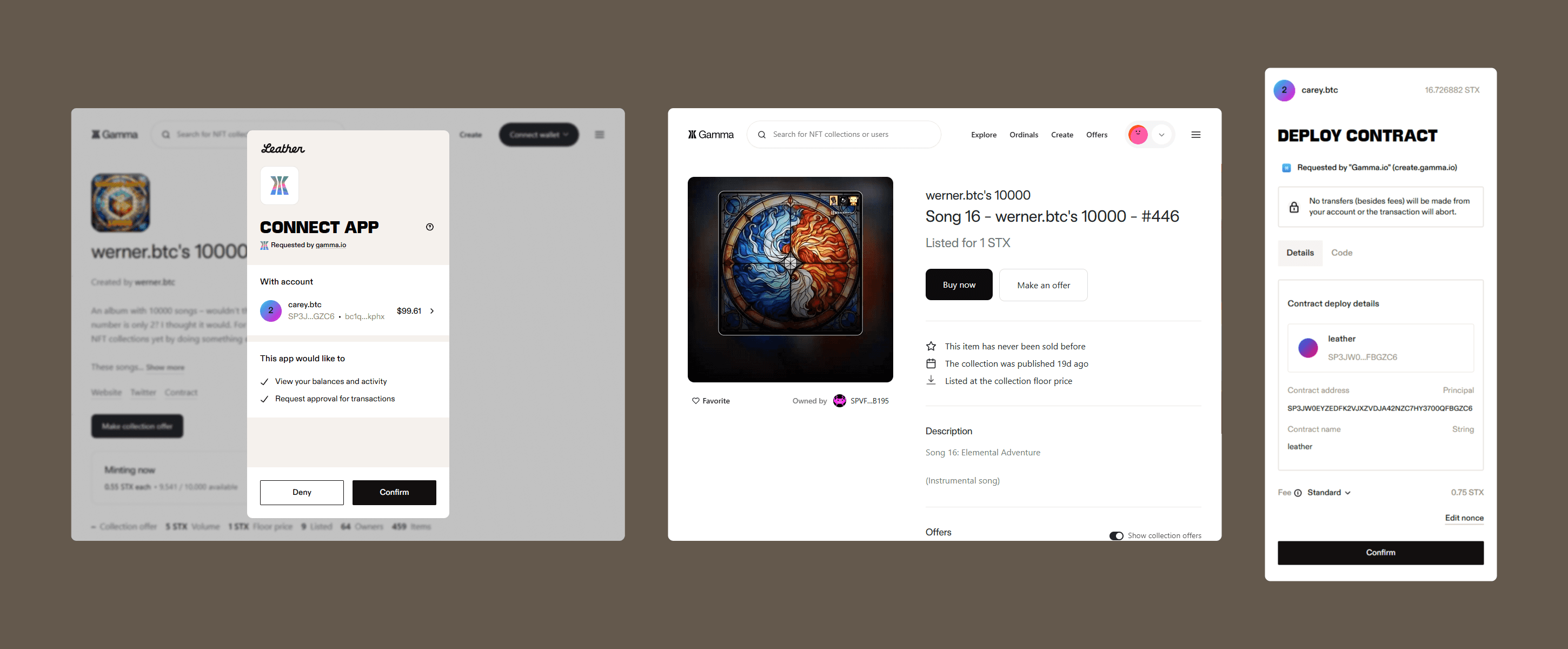
You don’t need to be an expert developer to mint Bitcoin NFTs on Stacks. There are NFT marketplaces that allow you to do it in an easy and straightforward way, simply connecting your Bitcoin wallet and following these simple steps:
- Set up your Stacks-compatible Bitcoin wallet, such as Leather.
- Fund your wallet with STX.
- Connect your Bitcoin wallet to Stacks NFT marketplaces such as Gamma or Magic Eden.
- Find the section for minting a collection.
- Provide the media and metadata that will be used to create your NFT.
- Deploy your smart contract to the network as indicated by the platform.
- Provide details to help collectors discover and mint your collection.
- Confirm and approve the transaction details and fees in your Bitcoin wallet.
- You have now minted your first Bitcoin NFT.

To buy or sell an NFT, simply
- Connect your Bitcoin wallet to the NFT platform.
- Explore the platform to find an NFT you like.
- Ensure you have enough STX on your wallet.
- Follow the steps on the platform and in your wallet to complete the purchase or sell an NFT you already own.
How Do You Mint Bitcoin Ordinals?
In the case of Bitcoin Ordinals, the data is stored directly and permanently on the Bitcoin layer thanks to a protocol based on Ordinal Theory. This protocol assigns a unique number to the smallest unit of Bitcoin—satoshis—in the order they are mined.
With this numbering system, individual satoshis can be tracked throughout the Bitcoin layer, which makes them all unique and completely different from each other (non-fungible).
Bitcoin Ordinals are not minted; they are inscribed. And so inscribing is the process of attaching the data to these numbered and trackable satoshis. This can also be done via NFT marketplaces, following the same steps as minting Bitcoin NFTs on Stacks, but keeping in mind that:
- Your files cannot exceed the size limitation of 4 MB.
- You will need to fund your wallet with BTC instead of STX.
Bitcoin NFT Use Cases
There are many use cases for Bitcoin NFTs, but these are the most common:
- Digital art and music tokenization
- Decentralized identity solutions
- Tokenization and ownership of real-world assets
- Digital collectibles
- Gaming assets
- Virtual real-estate ownership
- Cross-chain asset interoperability
- Access to decentralized finance (DeFi) applications
- Governance on Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
- Membership access to projects
- Event ticketing
How to Buy, Sell, and Trade Bitcoin NFTs with Leather
To buy, sell, and trade Bitcoin NFTs with Leather, follow these simple steps:
- If you don't have a Leather wallet set up, go to Leather’s website and download the Leather browser extension.
- Once installed, select "Create New Wallet" and follow the on-screen instructions. Make sure to back up your private keys securely to prevent loss of access. You can learn more about securing your Bitcoin wallet and opening a Bitcoin account here.
- After your wallet is created, fund it with some BTC or STX.
- Once funded, connect it to trusted Bitcoin NFT marketplaces like Gamma or Magic Eden.
- You will now be able to search available collections to buy and trade, as well as create and sell your own Bitcoin NFTs.
Bitcoin NFTs vs. Ordinals
While the term "Bitcoin NFT" is often used to refer to Ordinal inscriptions, it's important to know that the two are inherently different.
Bitcoin NFTs:
- Represent ownership of a specific digital item or piece of content.
- Can be traded, bought, and sold like traditional collectibles.
- Are minted by adding data about an asset to a smart contract on the Stacks blockchain.
- Store their data off-chain. Only a reference point is stored on-chain.
- Enable programmable features like royalties, interactive functionalities, and other complex interactions.
- Can only be non-fungible.
- Allow for larger files when minting.
Ordinals, on the other hand:
- Represent ownership of digital artifacts on the Bitcoin blockchain.
- Can be traded, bought, and sold like traditional collectibles.
- Are minted by inscribing (attaching) data about an asset to satoshis on the Bitcoin blockchain.All data is stored (inscribed) on-chain.
- Can be fungible or non-fungible.
- Have a file size limit of 4 MB per inscription, though developments like recursive inscriptions have addressed a number of challenges related to data size and Ordinals.
Are Bitcoin NFTs a Good Investment?
Only you can determine if Bitcoin NFTs are a good investment. Considering these factors will help you make conscious decisions:
- Bitcoin NFTs are expanding, allowing for considerable ecosystem growth and long-term potential.
- Bitcoin NFTs are secured by Bitcoin’s Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which has demonstrated exceptional resilience in comparison to other blockchains.
- Ordinals are stored directly on-chain, which makes them scarce and unique digital assets.
- On the flip side, price fluctuations can be common with Bitcoin NFTs.
- Ultimately, you need to think of why you want to own a particular Bitcoin NFT and assess if it would make a good investment based on that.
Why Are Bitcoin NFTs Rising in Popularity?
There are several reasons why Bitcoin NFTs are rising in popularity:
- The entire Bitcoin ecosystem is growing rapidly, which affects the growth of Bitcoin NFTs.
- They are fairly new to the ecosystem, and that brings attention from experienced and new users.
- They represent a novel way to create unique digital assets, offering new use cases.
- With Ordinals, users can store data directly onto the blockchain, which many consider beneficial.
- They are associated with Bitcoin’s brand and cryptocurrency, which is the most used and well-known of the entire crypto ecosystem.
- Many Bitcoin NFTs are tied to meme culture, which is very popular in the crypto space.
- After the Ethereum NFT boom, collectors and investors see Bitcoin NFTs as a good opportunity to diversify investments and explore other digital assets.
Disclaimer
Only you can determine if Bitcoin NFTs are a good investment.